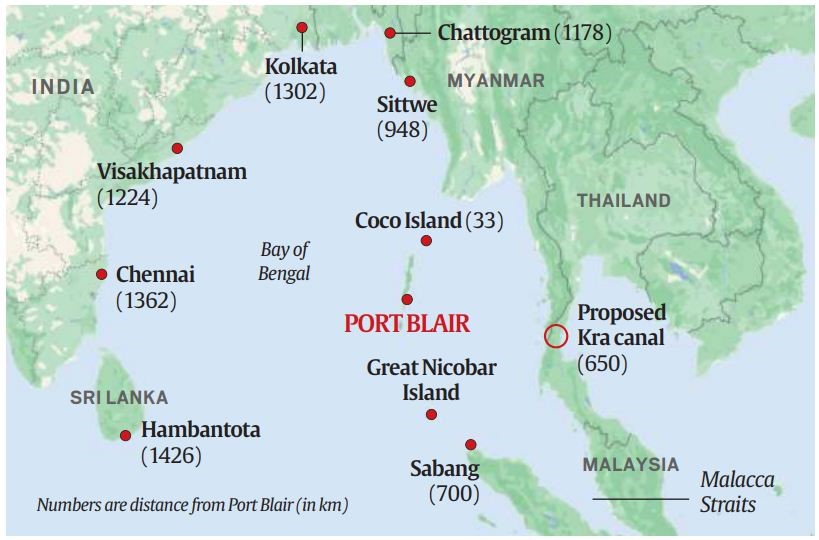
The new thrust on developing strategic infrastructure, both civilian and military, on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands has been long awaited.
|
Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
|
|
Strategic location |
Significance |
|
Sabang in Indonesia |
It is 90 nautical miles southeast of Indira Point (on Great Nicobar island) |
|
Coco Island in Myanmar |
It is barely 18 nautical miles from the northernmost tip of the Andamans. |
|
Kra canal to be built by Thailand |
The canal would connect the Gulf of Thailand with the Andaman Sea, its mouth would be about 350 nautical miles east of Port Blair. |
|
Malacca strait |
It connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific, is less than a day’s steaming from Port Blair. |
Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC), established as a tri-services command in 2001, plays a crucial role in safeguarding India's maritime interests.
Recently the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has issued further guidelines on its Green Credit Programme that will prioritise the restoration of ecosystem.
|
Green Credit Program (GCP) |
|
Previously, there was a requirement of a minimum of 1,100 trees per hectare for an area to qualify as reforested. However, the new guidelines allow flexibility, recognizing
References
Centre’s Patent (Amendment) Rules, 2024 has raised concerns about public health implications.
|
Status of patents in India |
|
Patent Act, 1970 is based on the recommendations of Bakshi Tekchand Committee (1949) and the Justice Rajagopal Ayyangar Committee
|
International obligations of India in patent system |
|
Now, Form 27 has to be submitted just once in three years and with no insistence of details
References
Childcare Leave
The Supreme Court recently said that two-year childcare leave, apart from mandatory maternity leave of 180 days is a constitutional right for woman employees.
Shalini Dharmani's plea –She told the court that she has exhausted her leaves and that the Himachal Pradesh govt had refused to grant her childcare leave as the state service rules do not have a provision akin to Section 43-C of the Central Civil Service (Leave) Rules.
Section 43-C of the Central Civil Service (Leave) Rules, 2010
Supreme Court’s recent judgment
References
Climate Strategy 2030
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) unveiled the Climate Strategy 2030 document on Earth Day recently.
India’s Green Financing Gap
NABARD's Climate Strategy 2030
|
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) |
|
Reference
The Hindu | Climate Strategy 2030
Mission ISHAN (One Nation, One Airspace)
India has kickstarted the process of unifying its 4 airspace regions into one spanning the entire nation.
References
Omorgus Moreshwar
Scientist Dr Aparna Sureshchandra Kalawate recently introduced a new species of beetles named Omorgus (Afromorgus) Moreshwar.

References
World Energy Congress & World Energy Council
India is showcasing its innovative technologies and power generation practices, at the 26th World Energy Congress, being held in Rotterdam, Netherlands recently.
About 26th World Energy Congress
About World Energy Council India
References
Preparing for the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) examination is a rigorous process that requires not just knowledge of various subjects but also a thorough understanding of current affairs. The UPSC syllabus covers a vast range of topics, and current affairs play a significant role in shaping the exam questions. Aspirants need to stay updated with the latest happenings in India and the world to crack the exam successfully. One of the most reliable sources of current affairs for UPSC is the IAS Parliament.
The IAS Parliament is a platform that provides the latest news and insights on Government Policies & Schemes, bills, and acts. It is an excellent resource for UPSC aspirants who want to keep themselves informed about the latest developments in Indian Politics, Indian Economy, and society. The platform provides regular updates on the functioning of the government and its various departments, making it an ideal source for current affairs preparation.
The IAS Parliament covers a wide range of topics, including agriculture, education, health, environment, technology, and more. Aspirants can access the platform through its website or app and stay updated with the Latest News and Information. The platform also offers a daily news digest, which summarizes the most important news of the day. This feature is particularly useful for those who are short on time and need a quick overview of the day and events.
In addition to news updates, the IAS Parliament also offers in-depth analysis and expert opinions on various issues. The platform has a team of experts who provide Insightful Articles on current affairs, which are beneficial for aspirants looking to develop a deeper understanding of a topic. These articles also help aspirants form an opinion on a particular issue, which is useful for the Essay Paper in the UPSC exam.
Apart from news and analysis, the IAS Parliament also provides resources for aspirants to enhance their knowledge of current affairs. The platform has a section on 'Current Affairs for UPSC,' which offers a comprehensive coverage of various topics such as Indian Polity, Economy, and International Relations. These resources are updated regularly, ensuring that aspirants have access to the latest information.
The IAS Parliament also offers a UPSC Quiz section, where aspirants can test their knowledge of current affairs. These quizzes are based on the latest news and help aspirants assess their level of preparation. Aspirants can also participate in UPSC Daily Quizzes and track their progress over time.
The IAS Parliament is an excellent resource for UPSC aspirants who are looking to stay updated with the latest developments in India and the world. The platform provides reliable and comprehensive coverage of current affairs, making it an ideal source for aspirants preparing for the UPSC exam. The resources offered by the platform are not just limited to news and analysis but also include quizzes and resources to enhance knowledge. The platform's user-friendly interface and regular updates make it a must-have resource for every UPSC aspirant.
In conclusion, keeping up with current affairs is a critical aspect of UPSC Preparation, and the IAS Parliament offers a reliable and comprehensive source for the same. Aspirants can leverage the platform's resources to stay informed and enhance their knowledge, making them better prepared to tackle the UPSC exam. IAS Parliament is a one-stop-shop for all UPSC aspirants looking for a comprehensive and reliable source of current affairs information.
Also Read: